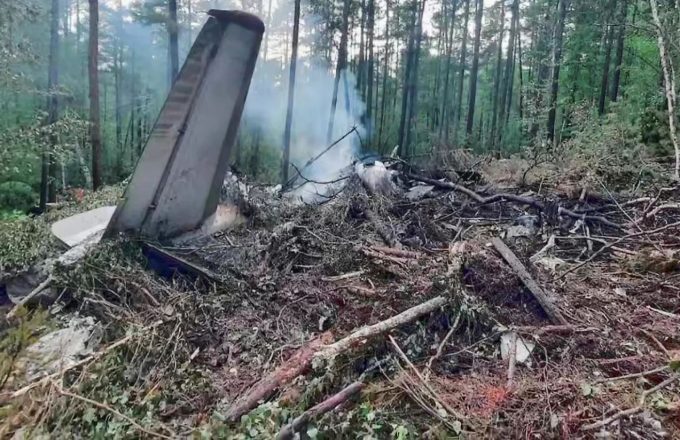
The launch of AMD’s Ryzen 9000 processors has not gone smoothly—and surprisingly, the main issue hasn’t been stock shortages, but a critical failure that’s rendering several chips unusable. Numerous users have reported that their CPUs have effectively burned out when used with certain motherboards, and all signs point to ASRock models as a likely culprit.
In the hardware world, protection mechanisms are designed to prevent exactly this kind of situation. However, they only work effectively when CPU and motherboard manufacturers coordinate their configurations properly. In this case, that synergy appears to have broken down, resulting in scenarios where both the processor and the motherboard are left damaged.
Concerns began mounting as users took to forums like Reddit to report how their Ryzen 9000 processors were being permanently damaged when paired with ASRock boards. This prompted Bryan, the content creator behind the Tech Yes City YouTube channel, to investigate the issue in depth.
Bryan tested several Ryzen 7000 and 9000 chips across motherboards from different manufacturers, and the findings were telling. ASRock boards appear to manage the CPU’s SoC (System on Chip) voltage in an unusual way—applying continuous and elevated fluctuations rather than stable delivery. While most motherboards regulate this voltage around 1.20V, ASRock’s models fluctuate between 1.250V and 1.270V.
Though this may seem like a minor difference, sustained overvoltage can cause accelerated wear and damage, especially when the processor itself is partly to blame by constantly requesting power. In essence, the issue stems from a combination of two security failures: the CPU asks for too much, and the motherboard delivers it without enforcing safety limits.
The investigation suggests this improper voltage management could be the direct cause behind the Ryzen 9000 failures when paired with certain ASRock motherboards. As reports continue to surface, the community is calling for a clear response from both ASRock and AMD to prevent further damage to users’ hardware.